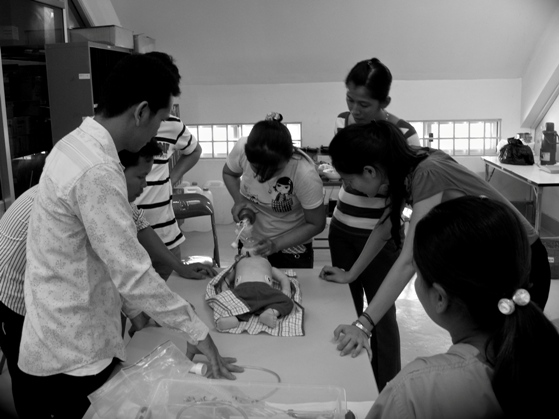
Saving Lives, Saving Vision
Retinoblastoma, the most prevalent malignant eye cancer among children, has a high incidence in the Philippines with a rate of 17.8 per million children aged 0 to 4 years. Given the country’s population of 92 million, of which 10 to 13% are children under the age of four, an estimated 210 cases are expected annually.
Retinoblastoma is highly treatable when detected early. However, the majority of Filipino cases present late, often with extra-ocular extension. This delay in diagnosis can be attributed to various factors, including financial constraints, limited access to healthcare and misdiagnosis.
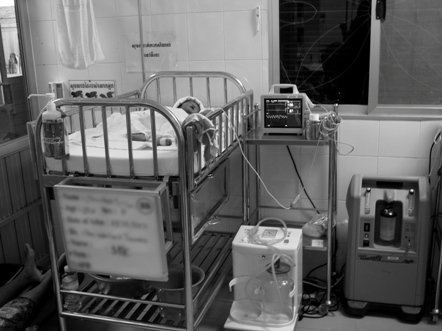
At the Southern Philippines Medical Center (SPMC), the tertiary referral centre for Mindanao, 93% of patients present with extra-ocular disease, resulting in a survival rate of less than 20%. The number of children diagnosed annually at SPMC is significantly lower than the expected 35 to 40 cases for the island.

In 2011, KTP-NUCMI funded a programme for the early detection of retinoblastoma in Davao city and other major cities on Mindanao Island. This collaborative effort involved the SPMC, led by Dr. Mae Dolendo, and NUH, in partnership with Dana Farber Children's Hospital Cancer Center and St. Jude Children's Research Hospital.
The programme’s key elements included raising awareness of early warning signs, establishing a referral system and developing a multidisciplinary team at the SPMC. Specific initiatives encompassed distributing educational materials such as posters and pamphlets on retinoblastoma in local health centres and conducting symposiums for barangay health workers (BHW), general medical practitioners, paediatricians and ophthalmologists.
The campaign covered Davao City, Tagum, General Santos City, Zamboanga City and Cagayan de Oro. To position the SPMC as a centre of excellence in retinoblastoma care, monthly online multidisciplinary tumour board meetings with the NUH team and world-renowned experts, Dr. Carlos Rodriguez-Galindo and Dr. Matthew Wilson, are held to discuss case management.
A retinoblastoma protocol and treatment plan were developed for SPMC, alongside a comprehensive database for monitoring care. Second opinions on pathology specimens and CT scans are provided by NUH. In 2012, a dedicated retinoblastoma centre was inaugurated at the SPMC.
Since the programme’s launch, retinoblastoma cases at the SPMC have doubled, with 20% now diagnosed at an early stage or intra-ocular stage. Building on this success, the programme is being replicated as a model in other key Mindanao cities and provinces, as well as in Metro Manila.
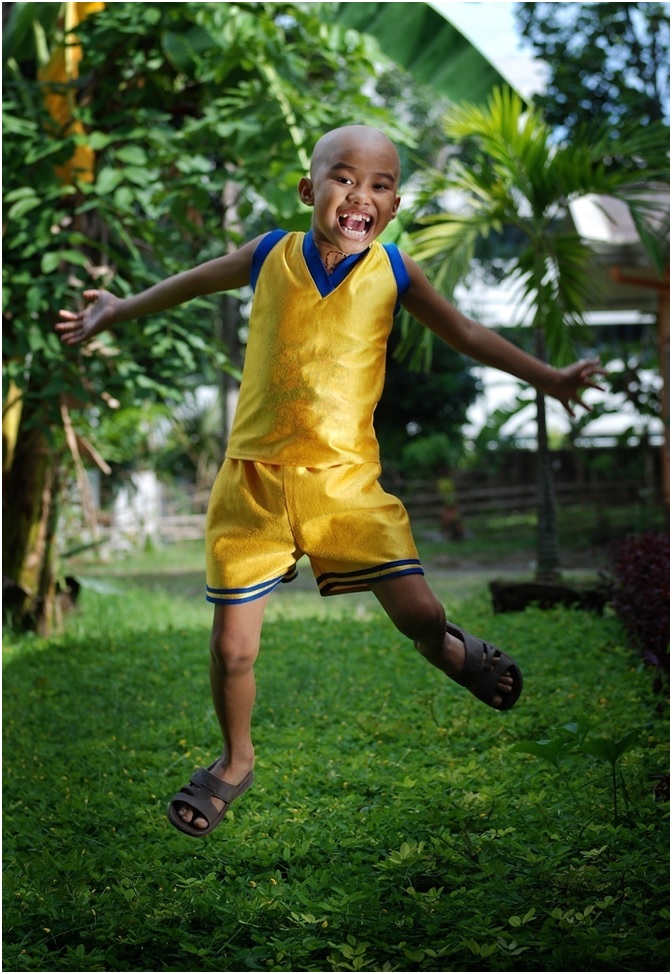

For the children in Mindanao afflicted with eye cancer, this initiative has been a beacon of hope. It has not only improved survival rates and the quality of life for these young patients and their families but also provided them with access to specialised cancer care that was previously beyond their reach.
Activities under the programme
- Educational campaigns
- Distribution of posters and pamphlets in hospitals and local health centres to educate the public
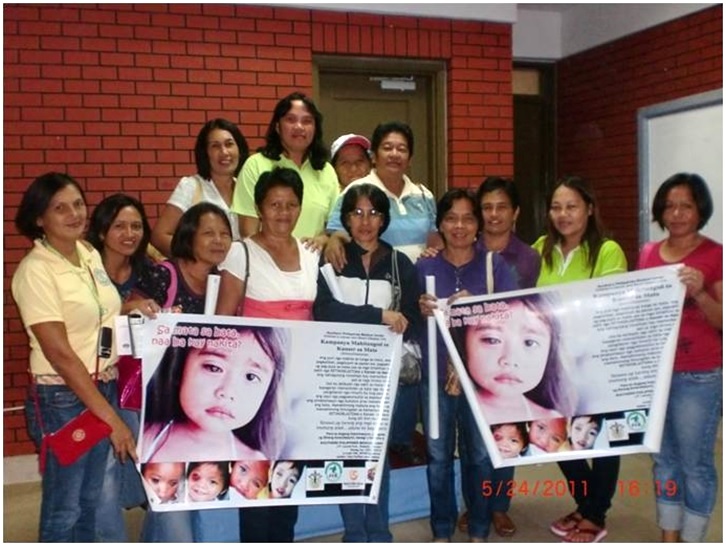


- Retinoblastoma symposium for medical professionals and health workers
- Establishment of data management system and registry of retinoblastoma patient monitor care for patients

- Mentorship programmes and Care4Kids teleconferences to impart knowledge and technology transfer
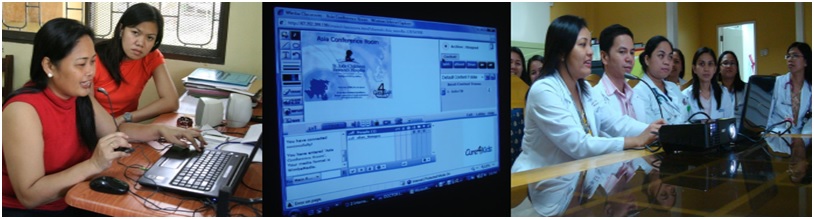
- Implementation of multidisciplinary meetings and clinical reviews to improve care for patients

- Psychosocial support for patients to help them cope with their illness


Acknowledgements
Project Leaders
Medical Advisors and Collaborators