Structured testing helps identify patterns and informs necessary adjustments for optimal glucose control. It is more effective than random testing. Consult your healthcare team for a tailored testing schedule and frequency, taking into account individual factors such as risk of hypoglycemia, medication type and adjustment needs. Discuss pre- and post-meal glucose targets with your healthcare team.
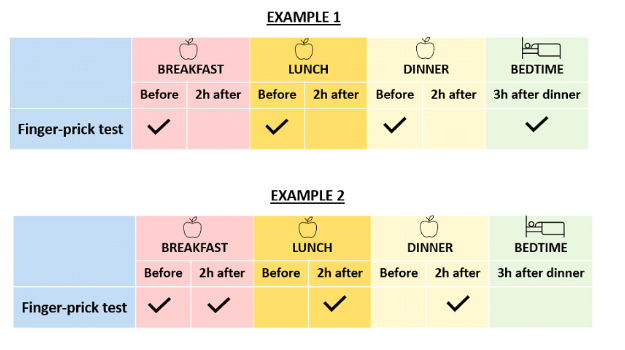
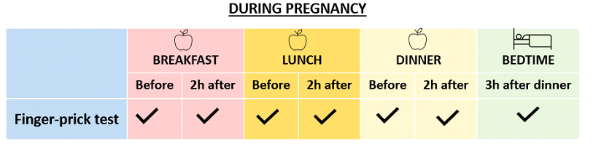
Additional testing situations:
- During illness:
Increase testing frequency (e.g., hourly or every 2 to 4 hours) when sick. Refer to Managing diabetes during sickness for more information. - Pre-exercise and during critical tasks: Especially important for those prone to low blood glucose
- Symptoms of low blood glucose: Test when experiencing symptoms such as dizziness, hunger and sweating



















