Following consultation and testing, a range of therapeutic options is considered.
Non-surgical Methods
1. Allergen Avoidance and Counselling
Primary treatments for allergic rhinitis are allergen avoidance and pharmacotherapy. Patients who do not achieve sufficient symptom relief through to allergen avoidance may benefit from medications, specific immunotherapy, surgery, or a combination of both, depending on their symptoms. Managing inhalant allergy includes counselling on proper environmental control and advice on allergy-reducing products. Based on allergy test results, our allergy nurses will provide strategies to minimise or avoid exposure to allergens.
For patients undergoing IPFT, allergy nurses will assist them in interpreting test results and emphasise the importance of dietary management. Patients are advised to avoid allergenic foods for a prolonged period to alleviate symptoms and improve their quality of life.
2. Medications
Nasal steroids and antihistamines are central to treatment of allergic rhinitis. Additional intranasal or intraocular medications may be prescribed as needed.
3. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy aims to gradually desensitise the body to the allergen, potentially modifying or suppressing the allergy response. It can be administered as medication placed under the tongue or through an injection under the skin, and involves:
An initiation phase, where the allergen dose is incrementally increased.
A maintenance phase, where the maximum tolerated dose is administered over an extended period, with regular follow-ups for a minimum of 3 years.
Surgery
1. Turbinate Reduction Surgery
This procedure reduces the size of the enlarged nasal turbinates (structures that help humidify and filter the air you breathe). It creates more space in your nasal passages, improving airflow while maintaining the natural function of the turbinates.
2. Septoplasty
A septoplasty is a surgical procedure to straighten a deviated nasal septum (the cartilage and bone dividing your nostrils), which can significantly improve airflow and reduce nasal obstruction.
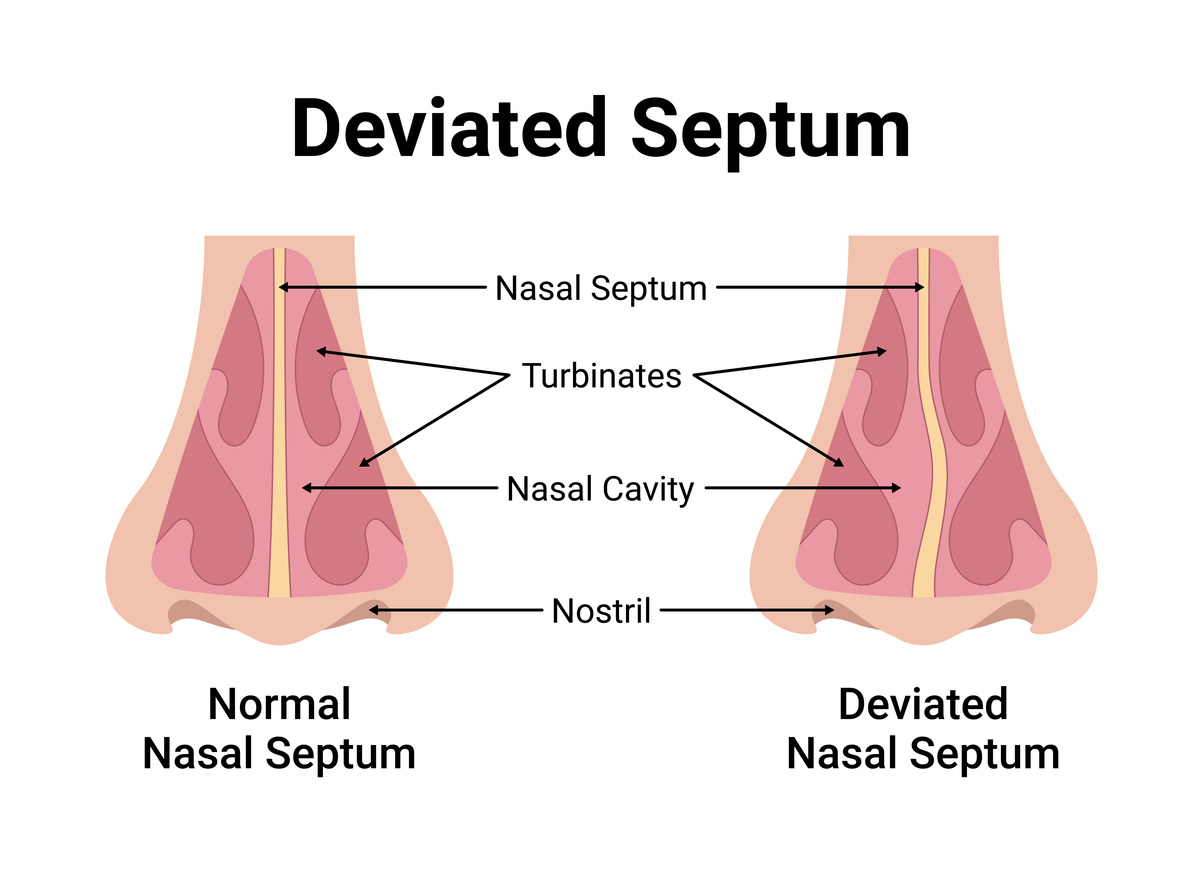
Straight Nasal Septum (Left) vs Deviated Septum (Right)
3. Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy is a minimally-invasive treatment that uses extreme cold to target and destroy overactive tissues in the nose, either under local or general anaesthesia. It is commonly used to treat conditions like chronic rhinitis by freezing the posterior nasal nerve or inferior turbinates. It also reduces inflammation and nerve sensitivity responsible for excessive mucus production and nasal congestion.





















