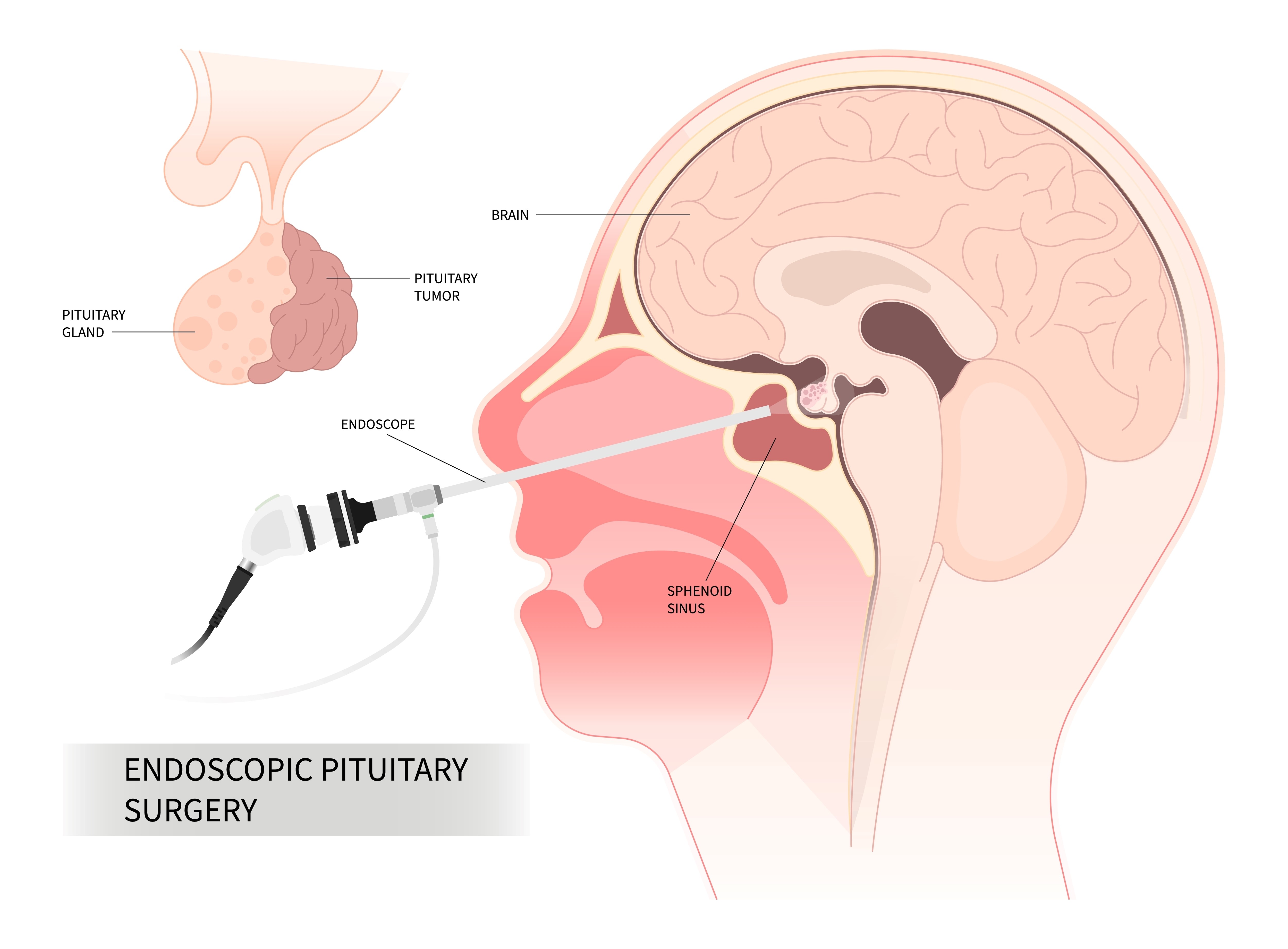
The endoscopic endonasal (a.k.a. transphenoidal) surgical approach uses the nostrils as a natural surgical corridor to remove pituitary adenomas, and many midline skull base, and brain tumours. This endonasal route is the preferred surgical approach for a large majority of pituitary adenomas and Rathke’s cleft cysts, as well as some of the craniopharyngiomas, clival chordomas and midline meningiomas.
With the use of high-definition endoscopy (surgical telescope), neuronavigation system (“GPS for the brain”) and carotid artery localisation with a doppler ultrasound; the endoscopic endonasal (a.k.a. transphenoidal) approach has evolved into a safe and effective technique in experienced hands. The major advantages of the endonasal (a.k.a. transphenoidal) route includes a high resolution, magnified view of the tumor and surrounding important structures, avoidance of brain retraction, minimal manipulation of the optic nerves, and no scalp/facial incisions.
The endonasal (a.k.a. transphenoidal) approach is not ideal for all midline tumours. In some patients, an alternative minimally invasive route such as the transorbital approach, the supraorbital eyebrow craniotomy or a conventional craniotomy may be recommended.